Yesterday I was talking to my friends on IRC about how I should use a proper RDBMS for ad hoc data analysis more often. Then I found myself a job.
The hard disks I use for my offsite backups are ready to be replaced. They are good reliable drives (Western Digital Ultrastar 8TB) but they have been in service for five years and the warranty is just about to expire.
So I wanted to get some new drives which will do me for the next five years. I needed to know: what are good reliable drives to buy?
It turns out Backblaze maintains Hard Drive Data and Stats.
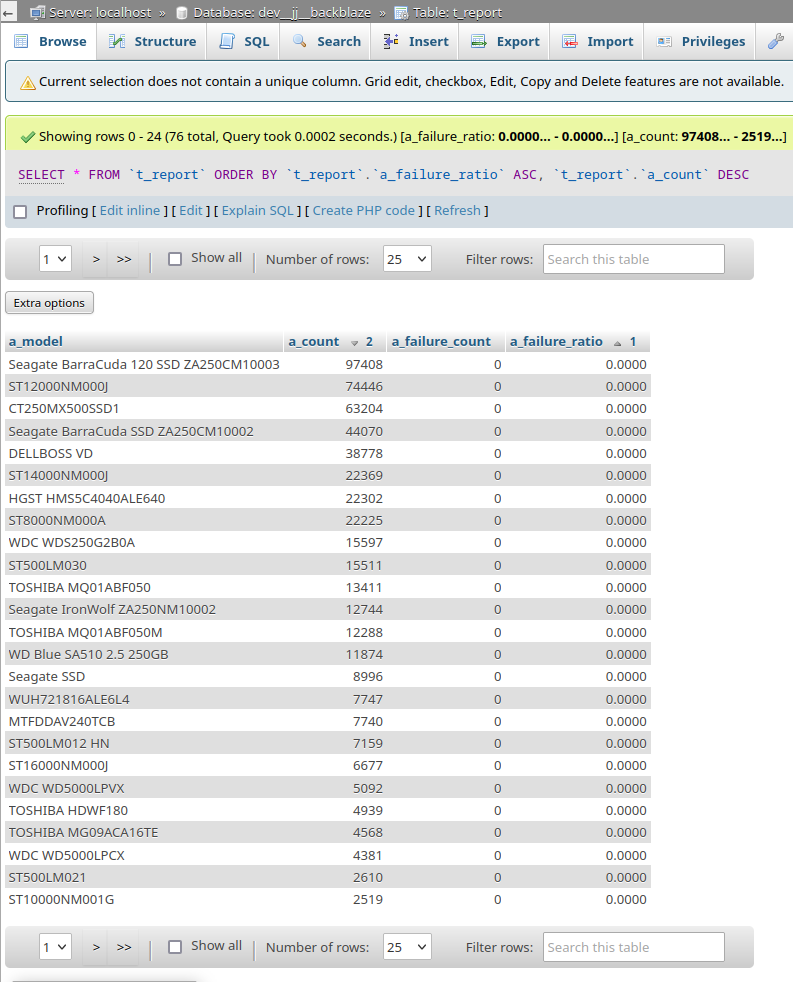
I downloaded their data for Q1 2025 and wrote a few scripts to process it. The output was this report:
The first drive listed in the above report is an SSD, but I want an ordinary spinning rust HDD. The second drive listed is ST12000NM000J which is Seagate Exos X18 12 TB. I found them on Amazon for AU$499 and on eBay for AU$280. So I purchased three drives from eBay.
Time well spent. Thanks d0nk`! <3